Conversational Medical AI: Ready for Practice
Overview
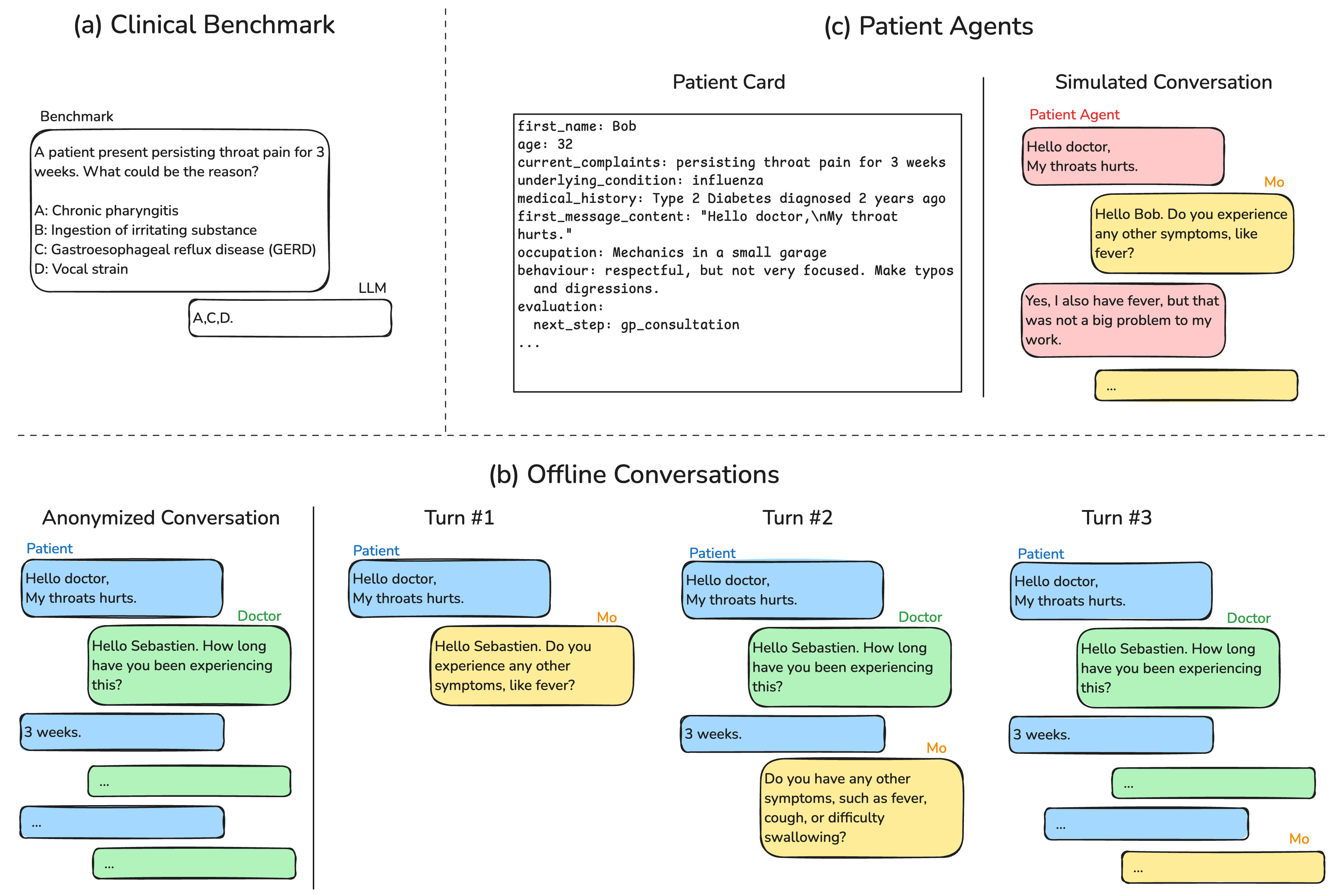
- Medical AI assistant named Mo deployed by Alan health insurance company
- Designed to handle medical conversations with real patients
- Built using large language models and custom medical knowledge
- Currently serving over 200,000 users in France
Plain English Explanation
Alan Health Insurance created an AI doctor's assistant called Mo that helps patients through text chat. Think of Mo as a very knowledgeable medical receptionist who can understand health questions and give helpful advice.
Mo works alongside human doctors rather than replacing them. When patients message the Alan app with health concerns, Mo helps gather information and provides basic medical guidance. For more serious issues, Mo connects patients with real doctors.
The system uses advanced AI technology similar to ChatGPT, but specifically trained on medical knowledge. Mo can understand medical terminology while still communicating clearly with patients in everyday language.
Key Findings
Medical conversational AI has reached a level where it can safely handle basic patient interactions. The research shows:
- Mo successfully manages 200,000+ patient conversations
- 92% user satisfaction rate
- Reduces doctor workload for routine cases
- Makes healthcare more accessible
- Maintains medical accuracy while using simple language
Technical Explanation
Mo uses a multi-stage architecture that combines several AI models:
- Initial language understanding model processes patient messages
- Medical knowledge model accesses verified health information
- Response generation model creates clear, accurate replies
- Safety checking system ensures advice stays within appropriate bounds
The system underwent extensive testing with synthetic patients before deployment. Medical professionals reviewed responses across thousands of test scenarios.
Critical Analysis
Some limitations exist:
- System cannot diagnose complex conditions
- Relies on patients accurately describing symptoms
- May miss non-verbal cues important in medical care
- Limited to text communication only
- Needs ongoing monitoring for accuracy
Further research should explore voice interaction capabilities and deeper integration with electronic health records.
Conclusion
AI-powered medical conversations show promise for improving healthcare access while maintaining quality. Mo demonstrates that carefully designed AI systems can safely handle routine medical communications, though human medical professionals remain essential for diagnosis and treatment.
The success of this deployment suggests similar systems could help address healthcare provider shortages and improve patient access to medical information. Future developments may expand capabilities while maintaining the crucial balance of convenience and safety.